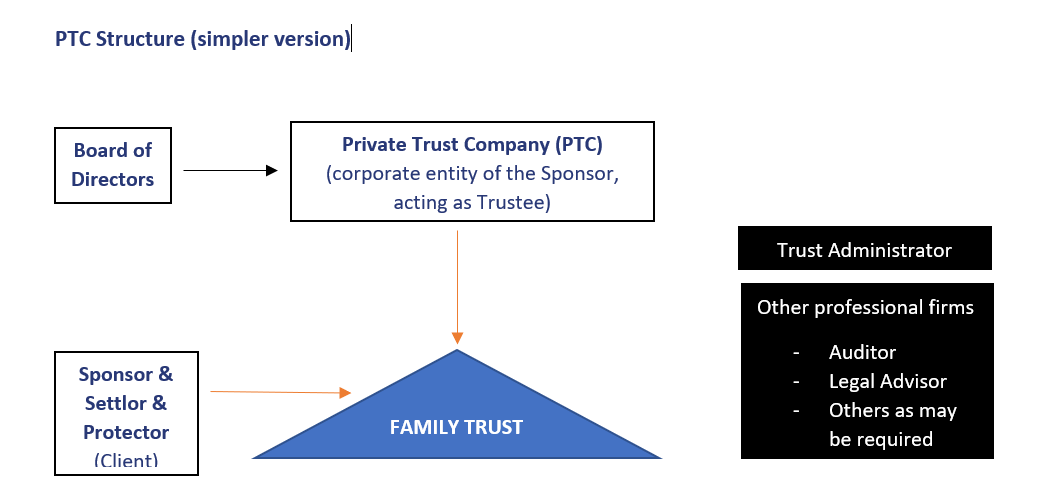
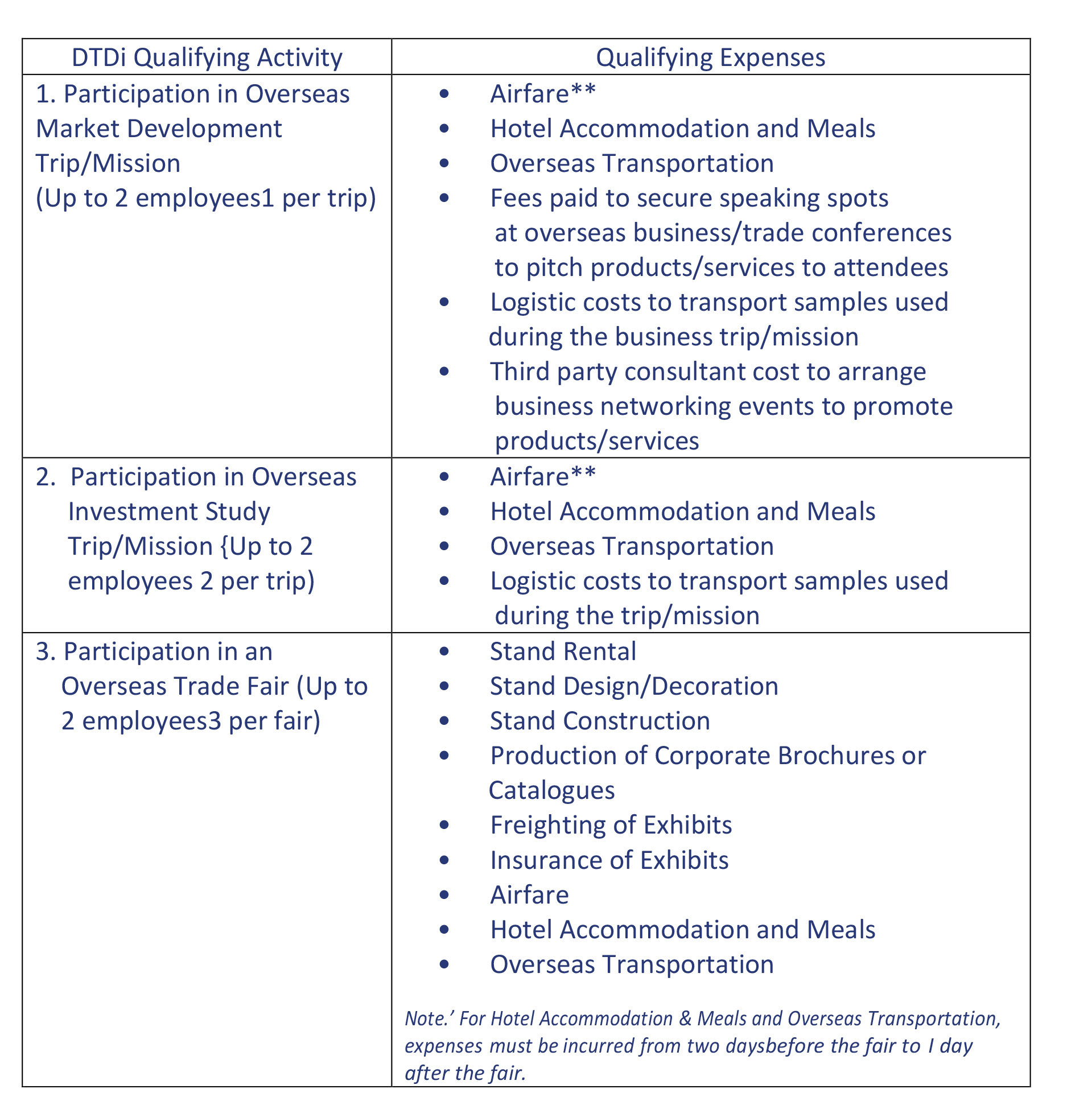
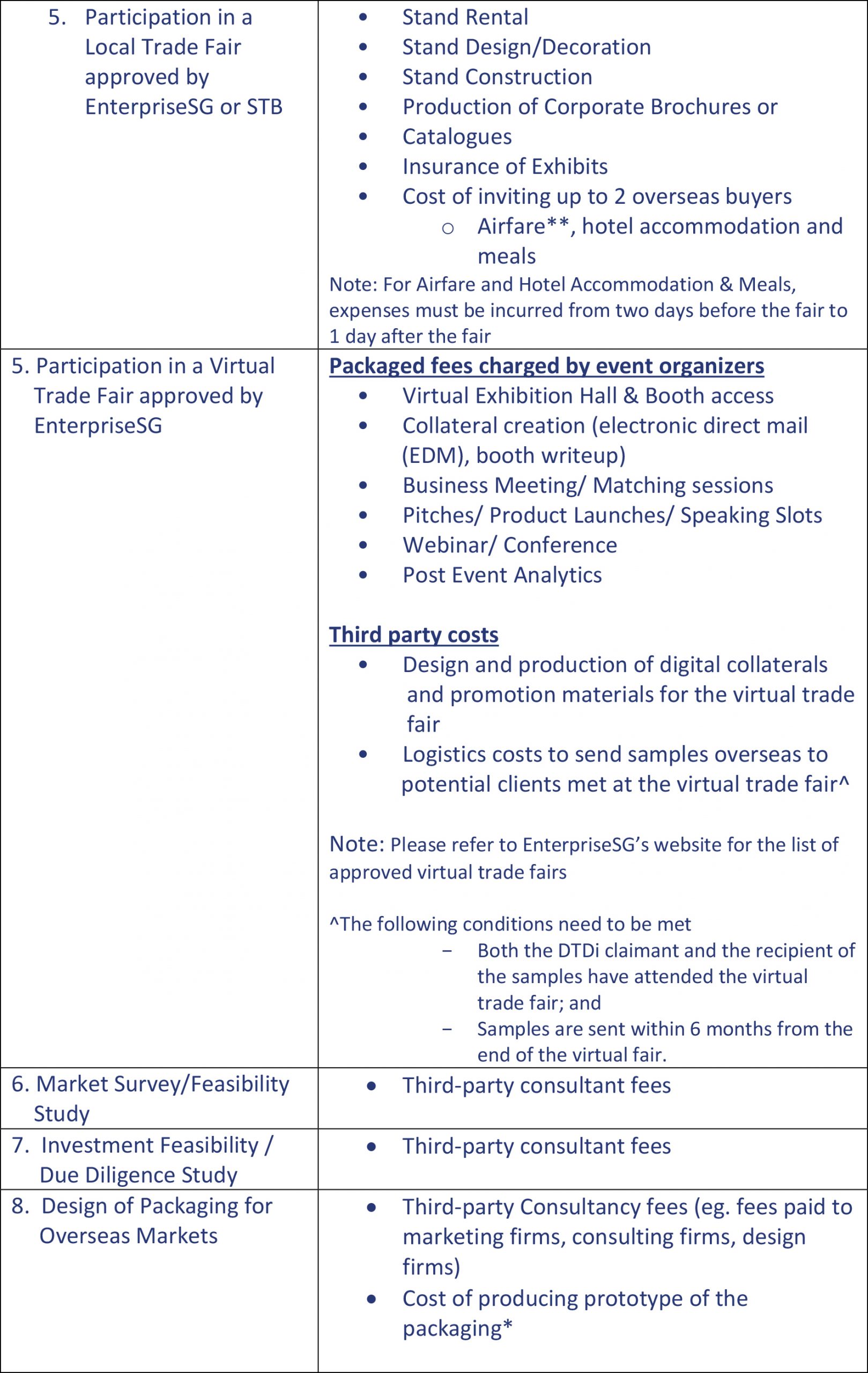
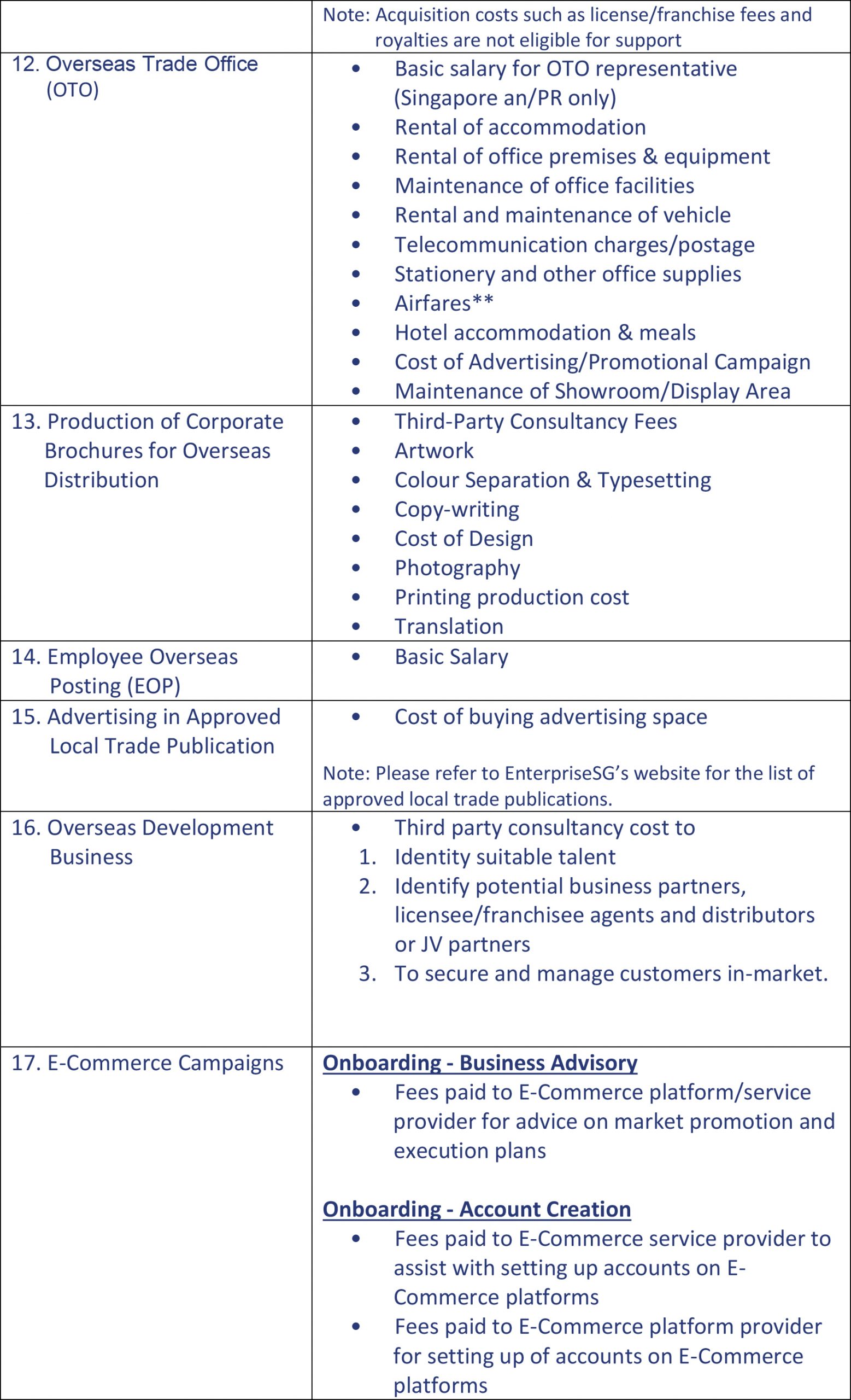
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Group of 20 (G-20) countries agreed to an overhaul of the international tax system, which will include a 15 per cent global minimum corporate tax on multinationals with annual revenue above €750 million (S$1.15 billion) which is going to take effect from 2023.
The tax reform also requires 25 per cent of profits from companies with €20 billion or more global annual turnover to be reallocated to jurisdictions where their customers are located. So far, 141 tax jurisdictions have agreed to implement the reform, which is designed to discourage multinationals from shifting profits to low-tax jurisdictions.
Asia has 48 countries and atleast 51 tax jurisdictions if Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan are included. Four of these are members of the OECD and six in the G-20. However, developing economies need not only more tax revenues to finance their budgets but also the flexibility to provide tax incentives to multinationals to attract investment that can generate employment and other economic benefits.
Policy makers may need to weigh the different considerations & design the tax policy to achieve a good balance across these competing norms. The global minimum tax rate & other provisions in the reforms are also aimed at putting an end to decades of tax competition between governments to attract foreign investment. Careful thought needs to be given to the impact on tax incentives in areas such as environment & climate change. OECD needs to ensure in particular that the global tax reforms do not remove the incentives needed to encourage research & development of emerging innovative technologies for the green economy.
Under BEPS (Base Erosion and Project Shifting), multinational enterprises (MNEs) with a global turnover in excess of 750 million euros (S$1.15 billion) that operate in jurisdictions that are subject to an effective corporate tax rate of less than 15 per cent will have to top up the taxes paid in those jurisdictions in their “home” jurisdiction. The top-up will be based on the difference between the corporate minimum tax of 15 per cent and the effective tax rate levied in that other jurisdiction.
When international tax rules are changed, the government will consider making changes to our corporate tax system accordingly, in consultation with businesses & tax professionals.
There are around 1,800 such MNEs in Singapore, and many pay effective tax rates of well below 15 per cent because of various tax incentives.
The corporate tax rates of some of neighboring countries are stated below for information:
| Country | % |
| Singapore | 17 |
| Malaysia | 25 |
| Indonesia | 25 |
| Hong Kong | 16.5 |
| Thailand | 20 |
| Vietnam | 20 |
| Cambodia | 20 |
| Laos | 35 |
Excerpts from Minister Lawrence Wong’s speech on the budget on 18th February, 2022 are as follows:
There are two pillars in BEPS 2.0. The first reallocates profit of the largest and most profitable multi-national enterprises (MNEs), from where activities are conducted to where consumers are located.
“There are ongoing international discussions on how to determine the jurisdictions which will surrender profits for reallocation to the markets under Pillar 1 & how much each will surrender. Given our small domestic market & the extent of activities conducted here by MNEs, Singapore will lose tax revenue under Pillar 1.”
The second pillar introduces the 15 per cent global minimum effective tax rate for MNE groups with annual global revenues of €750 million (S$1.1 billion) or more, under its Global Anti-Base Erosion (GLoBE) Model Rules, among other things.
“What this means is that if such an MNE were to have an effective tax rate of less than 15 per cent in Singapore at the group level, other jurisdictions such as its home jurisdiction can collect the difference up to 15 per cent.”
Singapore will adjust its tax System in response to Pillar 2 GloBE rules. It is exploring a top-up tax called the Minimum Effective Tax Rate, or METR which will top up the MNE groups’ effective tax rate in Singapore to 15 per cent.
The METR will apply to MNE groups operating in Singapore that have annual revenues of at least €750 million as reflected in the consolidated financial statements of the ultimate parent entity.
The Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore will study the tax rate further & consult industry stakeholders.

For further information please reach out to:
Mr. Rangarajan Narayanamohan,
FCA Senior Partner Natarajan & Swaminathan, Chartered Accountants, Singapore.
Email: ns@nsca.pro
Contact number: (65) 9832 3722
Address: 1 North Bridge Rd, #19-04, High Street Centre, Singapore 179094